TVS (Transient Voltage Suppressor) diodes are components used to protect sensitive components such as semiconductors. They are designed to limit the voltage within the circuit at a set voltage when there is a voltage surge. Their functions are similar to those of filters on air lines or water pipes.
TVS diodes are used in integrated circuits (ics) to protect against overvoltage, arc effects, rapid current changes (EFT), electrostatic discharge (ESD), induced load switching, and even lightning strikes.
The uses and application scope of transient voltage suppressors include protecting the following components and devices:
MOS memory
Telecommunication equipment
Microprocessor
Alternating current power line
Household electronic equipment
Compared with standard diodes, TVS diodes have a larger PN junction cross-sectional area, thus offering the following advantages: The large-sized design can safely guide a greater current to the ground, thereby minimizing potential hazards to the greatest extent. They can also respond quickly to high transient peaks, operate rapidly to suppress voltage and ensure circuit protection.
How does a TVS diode work?
Peak and overvoltage events may be caused by a variety of factors, including internal or external ones. Because some transient events are repetitive while others occur only once, it is difficult to predict them, and the duration and intensity of the transients can also vary greatly. Therefore, when a circuit is exposed to transient risks, TVS diodes are indispensable devices.
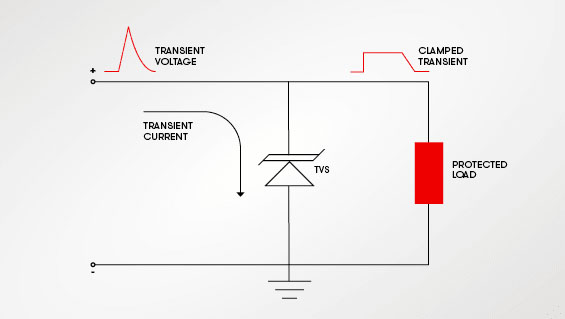
Transient voltage suppressors are usually connected in parallel with the circuit. They filter current to protect the circuit and can suppress any amount of voltage that can pass through the junction at any given time. This is very useful when a peak occurs. The clamping action then limits the voltage to a certain level and directs the excess voltage to the ground.
The working principle of TVS diodes
This figure shows the process by which TVS leads the transient current to the ground. It shows that the voltage observed by the protected load is limited by the clamping voltage level of the TVS.